2014.12.20
โปรแกรม Whitebox ช่วยในการเรียนการสอนโฟโตแกรม รีโมท
ถูกพัฒนาโดย Dr. John Linsay Department of Geography University of Guelph ที่ประเทศแคนาดา มุ่งเน้นทางด้านการประมวลผลข้อมูล DEM แล้วยังถูกพัฒนาให้สามารถนำมาใช้กับงานทางด้าน Geomatics มีการนำมาสอนในระดับบัณฑิตศึกษาเพื่อให้เข้าใจหลักการ โฟโตแกรม รีโมทเซนซิ่ง การประมวลผลข้อมูล Lidar
1. ฟังค์ชั่นในการประมวลผล ที่นี่
2. หน้าหลักของ Whitebox ที่นี่
น่าเอามาลองสอนนิสิตสาขาภูมิศาสตร์ที่ม.นเรศวร
วันเสาร์ที่ 20 ธันวาคม พ.ศ. 2557
ไพธอนไลบราลี่สำหรับสถิติเชิงพื้นที่
ไพธอนไลบราลี่สำหรับสถิติเชิงพื้นที่
เมื่อปี 2009-2010 ผมมีโอกาศได้สอนนิสิตเรื่องสถิติภูมิศาสตร์ ซึ่งถือว่าเพิ่งจบมาใหม่และไม่มีความเชี่ยวชาญ แต่ก็ได้มุมมองหลายอย่างจากอาจารย์พัฒนาและอาจารย์กัมปนาทว่าเราควรมีการสอนแลปนอกเหนือจากการคำนวนโดยมือ ผมได้ใช้ totorial ที่พัฒนาโดยภาษา Avenue โดยใช้โปรแกรม Arcview ในการสอน การเรียนการสอนเป็นไปได้ดีเพราะเป็นของแปลกสำหรับเด็กภูมิศาสตร์ป.ตรี แต่ก็มีความอึดอัดหลายอย่างที่ยังรู้สึกว่ายังไม่ดีต่อการพัฒนาต่อเมื่อเด็กไปใช้จริงในงานวิจัย หรือหากมีผู้สนใจนำไปใช้วิจัยเพราะเราไม่สามารถดัดแปลงได้ มาวันนี้มีไลบราลี่ที่ชื่อ Pysal มีผู้ร่วมคิดค้นคือ Luc Anselin’s group previously located at the University of Illinois,Champaign-Urbana, and Serge Rey who was at San Diego State University เป็นไลบราลี่ที่ใช้ในการประมวลผลสถิติเชิงพื้นที่ มีโมดูลดังนี้
pysal.cg — Computational Geometry
pysal.contrib - Contributed modules
pysal.core — Core Data Structures and IO
pysal.esda — Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis
pysal.examples — Data Sets
pysal.inequality — Spatial Inequality Analysis
pysal.region — Spatially constrained clustering
pysal.spatial_dynamics — Spatial Dynamics
pysal.spreg — Regression and diagnostics
pysal.weights — Spatial Weights
ไลบรารี่นี้เหมาะแก่นักศึกษาระดับบัณฑิตศึกษาอย่างมาก ในการวิจัยและพัฒนาต่อยอดในบ้านเรา แต่พื้นฐานไพธอน Unix โปรแกรมมิ่งควรจะมีพอได้บ้างก่อน จะดีมากๆ ดูเอกสารที่นี่
เมื่อปี 2009-2010 ผมมีโอกาศได้สอนนิสิตเรื่องสถิติภูมิศาสตร์ ซึ่งถือว่าเพิ่งจบมาใหม่และไม่มีความเชี่ยวชาญ แต่ก็ได้มุมมองหลายอย่างจากอาจารย์พัฒนาและอาจารย์กัมปนาทว่าเราควรมีการสอนแลปนอกเหนือจากการคำนวนโดยมือ ผมได้ใช้ totorial ที่พัฒนาโดยภาษา Avenue โดยใช้โปรแกรม Arcview ในการสอน การเรียนการสอนเป็นไปได้ดีเพราะเป็นของแปลกสำหรับเด็กภูมิศาสตร์ป.ตรี แต่ก็มีความอึดอัดหลายอย่างที่ยังรู้สึกว่ายังไม่ดีต่อการพัฒนาต่อเมื่อเด็กไปใช้จริงในงานวิจัย หรือหากมีผู้สนใจนำไปใช้วิจัยเพราะเราไม่สามารถดัดแปลงได้ มาวันนี้มีไลบราลี่ที่ชื่อ Pysal มีผู้ร่วมคิดค้นคือ Luc Anselin’s group previously located at the University of Illinois,Champaign-Urbana, and Serge Rey who was at San Diego State University เป็นไลบราลี่ที่ใช้ในการประมวลผลสถิติเชิงพื้นที่ มีโมดูลดังนี้
pysal.cg — Computational Geometry
pysal.contrib - Contributed modules
pysal.core — Core Data Structures and IO
pysal.esda — Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis
pysal.examples — Data Sets
pysal.inequality — Spatial Inequality Analysis
pysal.region — Spatially constrained clustering
pysal.spatial_dynamics — Spatial Dynamics
pysal.spreg — Regression and diagnostics
pysal.weights — Spatial Weights
ไลบรารี่นี้เหมาะแก่นักศึกษาระดับบัณฑิตศึกษาอย่างมาก ในการวิจัยและพัฒนาต่อยอดในบ้านเรา แต่พื้นฐานไพธอน Unix โปรแกรมมิ่งควรจะมีพอได้บ้างก่อน จะดีมากๆ ดูเอกสารที่นี่
ไพธอนไลบรารี่สำหรับ remote senseing and GIS (RSGISLib)
ไพธอนไลบรารี่สำหรับ remote senseing and GIS (RSGISLib)
ใช้ในการสอนในระดับปริญญาโทของมหาวิทยาลัย Aberystwyth ในรายวิชารีโมทเซนซิ่งและจีไอเอส
หลักๆใช้ไพธอน GDAL OGR โดยพัฒนาโมดูลในด้านการประมวลผลภาพและเวคเตอร์
เหมาะสำหรับนำมาใช้ในการเรียนการสอนวิจัยในระดับบัณฑิตศึกษาบ้านเรา น่าสนใจมว๊ากกกก
- คู่มือสำหรับใช้งานไลบราลี่และพื้นฐานไพธอน ที่นี่
ใช้ในการสอนในระดับปริญญาโทของมหาวิทยาลัย Aberystwyth ในรายวิชารีโมทเซนซิ่งและจีไอเอส
หลักๆใช้ไพธอน GDAL OGR โดยพัฒนาโมดูลในด้านการประมวลผลภาพและเวคเตอร์
เหมาะสำหรับนำมาใช้ในการเรียนการสอนวิจัยในระดับบัณฑิตศึกษาบ้านเรา น่าสนใจมว๊ากกกก
- คู่มือสำหรับใช้งานไลบราลี่และพื้นฐานไพธอน ที่นี่
วันศุกร์ที่ 19 ธันวาคม พ.ศ. 2557
บล๊อก shreshai for QGIS Python Matlab
บล๊อก shreshai for QGIS Python Matlab
มีเทคนิคที่จัดการด้านภาพได้น่าสนใจดีครับ ที่นี่
มีเทคนิคที่จัดการด้านภาพได้น่าสนใจดีครับ ที่นี่
ป.โท UCL สาขารีโมทเซนซิ่ง+ course materials
UCL สาขารีโมทเซนซิ่ง+ course materials (นี่คือสุดยอดต้นแบบที่บ้านเราควรจะดูไว้ในเรื่องการจัดการเรียนการสอน) MSc remote sensing
เป็นหลักสูตรปริญญาโทที่อยู่ในภาควิชาภูมิศาสตร์ของ UCL มีเนื้อหาให้อ่านตามรายวิชาที่เกี่ยวกับรีโมทเซนซิ่ง ทั้งเลคเชอร์ และ แลป ที่เน้นวิทยาศาสตร์ และการคำนวณข้อมูลโดยใช้ Python, IDL/ENVI น่านำไปปรับใช้สอนแนะนำ นักศึกษาในระดับป.โท/เอก โดยลิงค์เข้ากับภูมิอากาศ บรรยากาศศาสตร์ และโฟโตแกรมเมตรีได้เลย โดยเราสามารถศึกษาจากเนื้อหาที่เอาขึ้นเวปของ UCL ที่ทำไว้ดีมากๆ และที่น่าสนอีกอย่างคือการศึกษาที่เป็นแบบบูรณาการความรู้จากอาจารย์หลายภาควิชา with the Department of Civil, Environmental and Geomatic Engineering at UCL and the Department of Geography at Birkbeck College ต่างจากบ้านเรา ดังนั้นผู้ที่ได้ประโยชน์คือตัวนักศึกษา อ่านได้ ที่นี่
วิชาที่น่าสนใจได้แก่
1. Analytical and Numerical Methods
2. Scientific Computing
3. Principles and Practice of Remote Sensing
4. Image Understanding
5. Airbourne Data Acquisition
6. Global Monitoring of Environment & Society
เป็นหลักสูตรปริญญาโทที่อยู่ในภาควิชาภูมิศาสตร์ของ UCL มีเนื้อหาให้อ่านตามรายวิชาที่เกี่ยวกับรีโมทเซนซิ่ง ทั้งเลคเชอร์ และ แลป ที่เน้นวิทยาศาสตร์ และการคำนวณข้อมูลโดยใช้ Python, IDL/ENVI น่านำไปปรับใช้สอนแนะนำ นักศึกษาในระดับป.โท/เอก โดยลิงค์เข้ากับภูมิอากาศ บรรยากาศศาสตร์ และโฟโตแกรมเมตรีได้เลย โดยเราสามารถศึกษาจากเนื้อหาที่เอาขึ้นเวปของ UCL ที่ทำไว้ดีมากๆ และที่น่าสนอีกอย่างคือการศึกษาที่เป็นแบบบูรณาการความรู้จากอาจารย์หลายภาควิชา with the Department of Civil, Environmental and Geomatic Engineering at UCL and the Department of Geography at Birkbeck College ต่างจากบ้านเรา ดังนั้นผู้ที่ได้ประโยชน์คือตัวนักศึกษา อ่านได้ ที่นี่
วิชาที่น่าสนใจได้แก่
1. Analytical and Numerical Methods
2. Scientific Computing
3. Principles and Practice of Remote Sensing
4. Image Understanding
5. Airbourne Data Acquisition
6. Global Monitoring of Environment & Society
วันพฤหัสบดีที่ 7 สิงหาคม พ.ศ. 2557
ขั้นตอน-การประมาณค่าข้อมูลเรดาร์น้ำฝนด้วยวิธีการ Cressman1959
2014.08.07
ขั้นตอนการประมาณค่าข้อมูลเรดาร์น้ำฝนด้วยวิธีการ Cressman1959
หลังจากเขียนเล่มป.เอกติดขัดนิดหน่อย เลยหาลองเล่นการประมาณค่าเชิงพื้นที่อีกแบบ เผื่อเป็นการทบทวนไอเดียอะไรบ้าง ซึ่งการประมาณค่าข้อมูลเชิงพื้นที่มีหลายวิธีการแล้วแต่จุดประสงค์ของผู้ใช้งาน
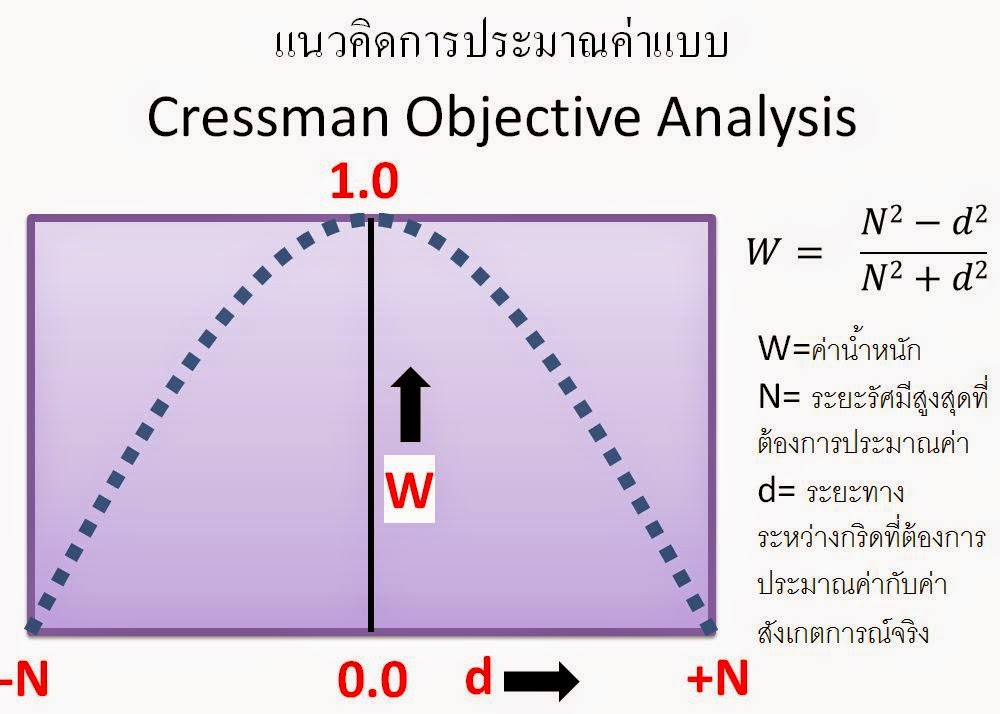
วิธีการประมาณค่าแบบที่พบเห็นได้บ่อยในทางอุตุนิยมวิทยาได้แก่ การประมาณค่า Objective analysis by Cressman interpolation เป็นวิธีการที่ใช้กับข้อมูลที่ได้จากการสังเกตในแนวแกน
X,Y,Z ซึ่งได้จาก Rewindsonde เช่น
ลมในแต่ละระดับความกดอากาศ ตามแนวคิดข้างล่างคือ ค่าน้ำหนักของข้อมูลที่ได้จากการสังเกตจะขึ้นอยู่กับระยะทาง
แนวคิด Cressman
ในการทดลองนี้ผมต้องการจะสร้างภาพตัดขวางแนวดิ่งของข้อมูลเรดาร์ที่สแกนแบบหลายมุมยก
จึงได้ประยุกต์ใช้วิธีการแบบ Cressman เข้าไปทำการให้ค่าน้ำหนักจุดเรดาร์ในแต่ละระยะทางของแต่ละมุมยก
คงมีคนสงสัยวิธีนี้แตกต่างอย่างไรกับ IDW ผมพอจะคิดได้ว่า สิ่งที่แตกต่างคือ Cressman จะให้ค่าน้ำหนักพร้อมกับทำให้เป็นน้ำหนักมาตรฐานในกริดนั้นๆเลย
สิ่งที่ง่ายและได้เปรียบ IDW คือเราไม่ต้องมาหาค่ายกกำลังที่เหมาะสมกับข้อมูล
เพียงแต่เราต้องหาว่าจะใช้รัศมีในแต่ละแกนอย่างไรให้เหมาะสมกับข้อมูลเราก็พอ โดยเราสามารถกำหนดรัศมี
Influence radius ได้ทั้สามแกน แต่ในที่นี้ผมกำหนดแค่สองแกนคือ
แนวแกน X,Z
เพราะเป็นภาพตัดขวาง วิธีการ Cressman นี้ยังเอามาใช้บ่อยๆในการประมาณค่าแผนที่ชนิด
CAPPI
ของเรดาร์หรือแผนที่แนวระนาบที่ระบุความสูงจากพื้นโลก ขั้นตอนการคำนวณหลักๆในโปรแกรม Fortran ของผมคือ
1.
อ่านไบนารี่จากข้อมูลเรดาร์ที่แสกนแบบหลายมุม
2.
ทำการวนลูปตามมุมยก
อซิมุทและระยะสังเกตของเรดาร์ เพือ
1.
หาพื้นที่ที่ต้องการประมาณค่าที่อยู่ในรัศมีที่ต้องการ
2.
คำนวนหาค่าน้ำหนักของค่าสังเกตที่มีต่อกริดนั้นๆ
3.
นำค่าน้ำหนักมาใช้กับค่าสังเกต รวมผลลัพธ์ของค่าน้ำหนัก
ค่าข้อมูลที่ถ่วงค่าน้ำหนัก ในแต่ละกริด
3.
ประเมินผลค่าการประมาณค่าด้วยการนำค่ารวมของข้อมูลถ่วงน้ำหนักหารด้วยค่ารวมค่าน้ำหนักทั้งหมด
4.
เก็บข้อมูลในรูปไบนารี่เพื่อแสดงผลในโปรแกรม NCL
การเปรียบเทียบการประมาณค่าแบบ Cressman VS IDW
ผมเปรียบเทียบผลลัพธ์ที่ได้4แบบ
โดยสามแบบแรกใช้ Cressman ในรัศมีที่ต่างกันออกไป
ส่วนแบบสุดท้ายเป็นผลมาจากวิธีการ IDW จะเห็นว่า แบบที่ใช้ Cressman ที่รัศมี 4
กม.ทั้งแนวแกน Xและ Z จะคล้ายคลึงกับ
IDW หากผลของ Cressman
มีความราบเรียบกว่าและคงค่าความแรงของฝน Convective เหมือนกันกับ IDW แต่โปรแกรมยังมี
Bug
อยู่ในเรื่องของขอบเขตสุดท้ายของการประมาณค่า ต้องปรับปรุงอีกหลายอย่าง
วันพุธที่ 6 สิงหาคม พ.ศ. 2557
ขั้นตอน-การประมาณค่าข้อมูลน้ำฝนจากเรดาร์ตรวจอากาศเพื่อสร้างภาพ RHI
2014.08.06
Squall line เป็นแนวฝนแบบ Convective
ที่จัดเรียงตัวกันในมาตราส่วน Meso scale คิดง่ายคือ
ประมาณหลักร้อยกิโลเมตรนั่นคือ
พื้นที่เรดาร์ตรวจอากาศภาคพื้นดินสามารถตรวจจับรูปแบบการเคลื่อนที่ของฝนนี้ได้
ในแถบอินโดจีนมีโปรเฟสเซอร์ Prof.Takehiko Satomura ได้ทำการอธิบายและเสนอกลไกการกำเนิดรูปแบบฝนชนิดไว้แล้ว
ในปี2000 น่าเสียดายที่ท่านได้จากโลกนี้ไปแล้วเมื่อเดือนมีนาคม 2014 ท่านเป็นอาจารย์ของผมเอง
หากแต่ไอเดียท่านยังอยู่กับพวกเรา
แนวคิดภาพตัดขวางแนวดิ่ง RHI
1.
อ่านเรดาร์แบบ Volume ไฟล์ และเลือกมุมอซิมุทที่ต้องการ Plot เลือกความสูง
ระยะทางของเรดาร์บีม
2.
คำนวนความสูงและระยะทาง ของแต่ละจุดที่เรดาห์ได้ทำการบันทึกข้อมูล
3.
เรียกซับโปรแกรมเพื่อประมาณค่าจุดเรดาร์ในแต่ละมุมยก ด้วย IDW
ตัวอย่างฝนชนิด Squalline
program
create_RHI
!-------------------------------------------------------------
! 2014.08.06 NATAPON MAHAVIK
! to create data for plotting Range-Height-Indicator [RHI]
! from extracted radar of
Phetchabun by Gematronik library
! data stor at
/home/mnattapon/RAID3storage4/research_icp/
!
analysis_phb_alg/radar_ans/cal_RHI_PPI_CAPPI_rad/cal_RHI
! data of selected azimuth will be
interpolate by IDW
!-------------------------------------------------------------
implicit none
integer,parameter ::
sizeofreal=4 !-record size
integer :: i,j,m,n
real, parameter :: pi =
4*atan(1.0) !- exploit intrinsic
atan to generate pi
real,parameter ::
d2r=pi/180.0 !- radian
conversion degree to radian
real,parameter :: k2m=1000.0 !- km to meters
real,parameter :: NA=-9999.0 !- no radar data
!-radar variables
integer :: rn !-record number
integer :: maxelv !-max number of
elevations
real :: elv_rad ! elevation
angle in radian
character*10 :: path
real :: rgate ! real(igate) = gate "km"
real :: rbin ! real(irbin) = rbin "km"
integer :: ielv, iazm, ibin
integer :: maxazmt !-Max number of
rays as temp var
integer:: maxbin ! Max number of
range
integer,parameter ::
maxazmf=1000 !-Max number of
rays as my asssumption!!!
real, dimension(:,:,:), allocatable
:: rdata !-Radar data
real, dimension(:,:),
allocatable :: elv !-Elevation angles
real, dimension(:,:),
allocatable :: azmth !-Angles [ in mathematic in degree]
real,dimension(:,:), allocatable
:: azmth_rad !-Angles [in azimuth in
radian]
integer,dimension(:),allocatable
:: maxazm !-Max number of rays
depending on sweeps
real,dimension(:,:,:),allocatable
::beam_dist_hz !-beam distance in
horizontal plain in m.
real,dimension(:,:,:),allocatable
::beam_height !-beam height by reinhart
p62 in m.
integer,parameter::re=6374000. !-earth radius in m.
real,parameter ::rr=4./3.*re !-reinhart p62 as R' in
m.
real,parameter :: rad_alt=97. !-radar altitude above MSL
from calculation DEM.(GG~73)
real :: h_rd=30. !-height of
radar antenna by estimate TMD using 30m
integer :: az_int !-round up real azimuth to interger [degree]
real,parameter :: sel_az=225.0 !-selected azimuth degree
real,parameter ::
min_dbz=10.0,max_dbz=100.0 !-max and
min dbz
real,parameter :: max_dist=200.0 !-max distance for RHI in km
real,parameter :: max_high=15.0 !-max hight for RHI in km
!-output var for interpolation
real, dimension(:,:), allocatable
:: dbz !-dbz at elevation(i) & bin number(i) [dBZ]
real, dimension(:,:), allocatable
:: height !-height from ellipsoid
at elevation(i) & bin number(i) [km]
real, dimension(:,:), allocatable
:: dist_x !-distance from radar
site at elevation(i) & bin number(i)[km]
real, parameter :: res=1.0 !- unit in km
integer,parameter :: nx=max_dist/res !- number of x pixels
integer,parameter ::
ny=max_high/res !- number of
y pixels
real, dimension(nx,ny)::
outp_intp !- interpolated
output
real, parameter :: radi=2.0 !-radius of interpolation
in idw [km]
!-read radar binary
!-cut
rn=1
open(10,file=trim(path)//'PHB1008102100.dat',form='unformatted',access='direct',recl=sizeofreal)
read(10,rec=rn) maxelv
!-cut
!-initialize output
dbz=NA;height=NA;dist_x=NA
do ielv = 1, maxelv
maxazmt=maxazm(ielv)
do
iazm = 1, maxazmt
read(10,rec=rn) azmth(iazm,ielv)
rn = rn + 1
!--- convert azmuth to be mathematic angle
!-cut
read(10,rec=rn) elv(iazm,ielv)
rn = rn + 1
do ibin = 1, maxbin
read(10,rec=rn) rdata(ibin,iazm,ielv)
rn = rn + 1
!-cal beam position in horizontal plain
!-cut
!-cal beam height + rad altitude in meter.
!-cut
endif
end do
end do
end do
close(10)
!-call sub IDW interpolate_idw(dbz(height,dist))
print*,'interpolate dbz to idw of
range-height radar ...'
call interpolate_idw(dbz,height,dist_x,maxelv,maxbin,res,nx,ny,radi,max_dbz,outp_intp)
print*,'infos for GRADS ;)
xdef:',nx,'ydef: ',ny,'resolution: ',res
!-write interpolated radar RHI to binary for checking in grads
open
(20,file='rs_interpolated_RHI_radar.bin',form='unformatted',access='direct',
recl=nx*ny*sizeofreal)
write(20,rec=1)outp_intp
close(20)
open
(30,file='rs_interpolated_RHI_radar_ncl.bin',form='unformatted')
write(30)outp_intp
close(30)
deallocate(beam_dist_hz,beam_height);deallocate(rdata,elv,azmth,azmth_rad)
deallocate(maxazm);deallocate(dbz,height,dist_x)
end
program create_RHI
Subroutine
interpolate_idw(dbz,height,dist_x,maxelv,maxbin,res,nx,ny,radi,max_dbz,outp_intp)
implicit none
!-external
integer,intent(in) ::
maxelv,maxbin
real,dimension(maxelv,maxbin),intent(in)
:: dbz,height,dist_x
real,intent(in) :: max_dbz
real,intent(in) :: res !-defined resolution of output grid
[km]
integer :: nx,ny
real,dimension(nx,ny),intent(out)
:: outp_intp
real :: radi !-defined radius for interpolation [km]
!-internal variables
real :: dist !-distance between output grid
and input grid
integer :: sx,ex,sy,ey !-start and end grid of considering box
respected to radius
integer :: i,j,m,n
real,parameter :: NA=-9999.0 !-not
available data
real,parameter :: p=-2 !-power for idw
integer :: x,y !-coordinate of output grid in
input data grid
real :: inv_d !-inverse distance
real :: nw !-normalized weight
real,dimension(nx,ny) ::
sum_invd !-sum inverse distance
real,dimension(nx,ny) ::
sum_nw !-sum normalized weight
!-loop elvation and bin of input data to be fast calculate
!outp_intp=NA
!-1st loop for find summation of inverse distance in output grid
do i=1,maxelv
do j=1,maxbin
if (dbz(i,j)==NA)cycle
!-find box of considering interpolation respected to defined radius
sx=((int(dist_x(i,j))-radi)/res)-res; ex=((int(dist_x(i,j))+radi)/res)+res
sy=((int(height(i,j))-radi)/res)-res; ey=((int(height(i,j))+radi)/res)+res
!-here to avoid error outbound otherwise
segmentation fault
if (sx<=0) sx=1; if (ex>nx) ex=nx; if (sy<=0) sy=1; if (ey>ny) ey=ny
!-loop inside box for calculate summation of inverse distance
do m=sx,ex
do n=sy,ey
!-convert coordinate considering
grid to be same input coordinates
x=(m*res)-res+1; y=(n*res)-res+1
!-calculate euclidean distance
dist=sqrt(abs(x-dist_x(i,j))+abs(y-height(i,j)))
!print*,x,y,dist
!-cal inverse distance and sum all
inverse distance
inv_d=dist**p
sum_invd(m,n)=sum_invd(m,n)+inv_d
enddo
enddo
enddo
enddo
!-2nd loop apply normalized weight to dbz and sum all results of each
ouput grid
do i=1,maxelv
do j=1,maxbin
if (dbz(i,j)==NA)cycle
!-find box of considering interpolation
respected to defined radius
sx=((int(dist_x(i,j))-radi)/res)-res; ex=((int(dist_x(i,j))+radi)/res)+res
sy=((int(height(i,j))-radi)/res)-res; ey=((int(height(i,j))+radi)/res)+res
!-here to avoid error outbound otherwise segmentation fault
if (sx<=0) sx=1; if (ex>nx) ex=nx; if (sy<=0) sy=1; if (ey>ny) ey=ny
!-loop inside box for calculate weight, then apply it
do m=sx,ex
do n=sy,ey
!-convert coordinate considering grid to be same input
coordinates
x=(m*res)-res+1; y=(n*res)-res+1
!-calculate euclidean distance
dist=sqrt(abs(x-dist_x(i,j))+abs(y-height(i,j)))
!-cal inverse distance, normalize and sum all weighted
dbz
inv_d=dist**p
nw=inv_d/sum_invd(m,n)
sum_nw(m,n)=sum_nw(m,n)+nw !-it must be 1.0 in every
grid
outp_intp(m,n)=outp_intp(m,n)+(nw*dbz(i,j))
enddo
enddo
enddo
enddo
!-replace values for grads or NCL plot
where (outp_intp>max_dbz)
outp_intp=0
endwhere
End subroutine interpolate_idw
5.
ตัวอย่างโค้ดของ NCL .ในการ Plot ภาพ RHI โปรแกรมนี้มีอะไรน่าตื่นเต้นเยอะนะครับ
ช่วยในงานวิจัยได้ไม่น้อยเลยครับ
;**********************************************************************
; color_1.ncl
; NATTAPON MAHAVIK
; Concepts illustrated:
;
- Drawing color filled contours using the default color map
; how to read and write data from
f90 to ncl
;
https://www.ncl.ucar.edu/Document/Functions/Built-in/fbinread.shtml
;
;**********************************************************************
load
"$NCARG_ROOT/lib/ncarg/nclscripts/csm/gsn_code.ncl"
load
"$NCARG_ROOT/lib/ncarg/nclscripts/csm/gsn_csm.ncl"
;************************************************
begin
;************************************************
; read in binary
;************************************************
fili="rs_interpolated_RHI_radar_ncl.bin"
recl=200*15
;rad =
fbindirread("rs_interpolated_RHI_radar_ncl.bin",rec,(/15,200/),"float")
r=fbinread (fili, recl , "float")
rad=onedtond(r,(/15,200/))
rad@_FillValue = -9999 ;missing values
;************************************************
; create plot
;************************************************
wks = gsn_open_wks("ps","ps_RHI_radar_PHB") ; open a ps file
gsn_define_colormap(wks,"prcp_1") ; choose color map
res =
True ; plot mods desired
res@vpWidthF = 0.8 ; set width and height
res@vpHeightF = 0.5
res@cnFillOn =
True ; turn on color fill
res@gsnMaximize = True
res@gsnDraw =
False ; don't draw
yet
res@gsnFrame =
False ; don't
advance frame yet
res@cnInfoLabelOn =
False ; not show infomation height
res@cnLineLabelsOn =
False ; not show label
of contour line
res@cnConstFLabelOn = False
res@cnLineThicknessF = 0 ; change line thickness
res@cnLinesOn = False
res@tiMainString =
"Range Height Indicator of Squallline in Thailand"
res@tiXAxisString =
"Distance [km]"
res@tiYAxisString =
"Height[km]"
res@cnLevelSelectionMode = "ManualLevels" ; manually set the contour levels with
the following 3 resources
res@cnMinLevelValF = 10.0 ; set the minimum contour
level
res@cnMaxLevelValF = 60.0 ; set the maximum contour
level
res@cnLevelSpacingF = 5.0 ; contour interval
res@lbOrientation = "vertical" ; vertical label bar
res@lbLabelStride = 2.0
res@gsnSpreadColors=True
plot = gsn_csm_contour(wks,rad,res)
draw(plot) ; note
we are drawing the first one!
frame(wks)
end
สิ่งที่ต้องทำต่อไปคือ แก้โปรแกรมให้ยืดหยุ่น ใช้กับข้อมูลหลายช่วงเวลา นำวิธีการประมาณค่าแบบอื่นๆมาใช้
สมัครสมาชิก:
ความคิดเห็น (Atom)